2016-2017 Materiality Assessment
Updated responsibility & sustainability non-financial materiality assessment highlights Nielsen’s responsibility to its stakeholders
In 2016 and 2017, we updated our non-financial materiality assessment, using the original findings from our first assessment conducted in 2014 and 2015 as a starting point. This new assessment follows the guidance provided by the Global Reporting Initiative’s new Standards, formally introduced in 2016. As part of our reporting process, we are also including an update on how we responded to stakeholder feedback from the previous assessment, along with an updated look at Nielsen’s strategic priorities and driving forces for the years ahead.
More information about our ongoing stakeholder engagement efforts and our global environmental, social and governance (ESG) approach can be found in our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report, published in May 2016. At Nielsen, we broadly define “corporate responsibility and sustainability” across the relevant ESG aspects of the company, including but not limited to, the impact of our efforts related to Global Responsibility & Sustainability, Diversity and Inclusion, Human Capital Development, Supply Chain Sustainability and our overall business performance across all teams, geographies and functions.
As it was before, our intentions in opening up the non-financial materiality process to all stakeholders is to incorporate this feedback into our overall processes, business strategy, and corporate responsibility and sustainability programs. Beyond seeking to better understand how stakeholders view Nielsen today, we also used the feedback to identify potential risks and opportunities both generally and in terms of our ESG goals, and any emerging issues that could affect Nielsen’s business success and stakeholder relationships in the future. Good governance, trust, and a commitment to transparency came up as dominant themes throughout this process. Our willingness to seek inputs from all stakeholders is aligned with Nielsen’s overarching values of being open, connected, useful and personal. Our final list of material issues also led us to identify tangible goals which are introduced in this document. We define issues in this context as positive opportunities for continued growth.
One of the major issues that came up throughout all of our stakeholder interviews and research was the fundamental importance of trust and transparency to Nielsen’s business. Transparency is essential to maintaining the foundation of trust we have established with our clients and other stakeholders over the course of our 94-year history. This trust is rooted in our strong integrity, the soundness of our research methodologies, data and insights, and the high quality of our processes and quality assurance controls. We also recognize the value of transparency in our collaborations with strategic partners and clients across our business; it is critical that both trust and transparency are embedded throughout this collaborative approach to ensure that our values are never compromised in any way. In this way, trust and transparency are a key part of each of the issues included in this non-financial materiality assessment.
We heard from our stakeholders throughout this process that they want to continue to learn more about areas like Nielsen’s involvement with and use of new innovation, employee retention strategies, and environmental impact. Nielsen is committed to continuing our practice of open and ongoing stakeholder engagement and dialogue, including through these regular non-financial materiality assessments and future updates to our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Nielsen plans to use feedback from this assessment and ongoing stakeholder engagement to ensure continued progress in these and other areas. We also plan to publish an updated Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)-aligned report in 2018.
Stakeholder feedback
To determine the top material issues affecting our stakeholders, society, the environment, and Nielsen, the Nielsen Global Responsibility & Sustainability team collaborated with cross-functional groups across the business to solicit and review feedback from all of Nielsen’s key stakeholder groups, both directly and, in some cases, through proxies. These groups include but are not limited to: employees, investors, clients, industry trade groups, suppliers, strategic business partners, industry influencers, value-added resellers, regulators and policy influencers, and non-governmental and community organizations. We specifically sought out new internal and external perspectives to ensure input was appropriately balanced, and we also engaged stakeholders across a wide range of geographies. We reviewed stakeholder feedback through a variety of different forms, including but not limited to: existing documentation, web commentary, webinars, surveys, social and traditional media content, as well as through more than 40 in-depth virtual and in-person interviews and focus groups. While we seek to continuously engage stakeholders in a variety of ways, we made a concerted effort to engage stakeholders through this process to get focused feedback on our long-term strategy, goals, challenges, and opportunities.
Analysis
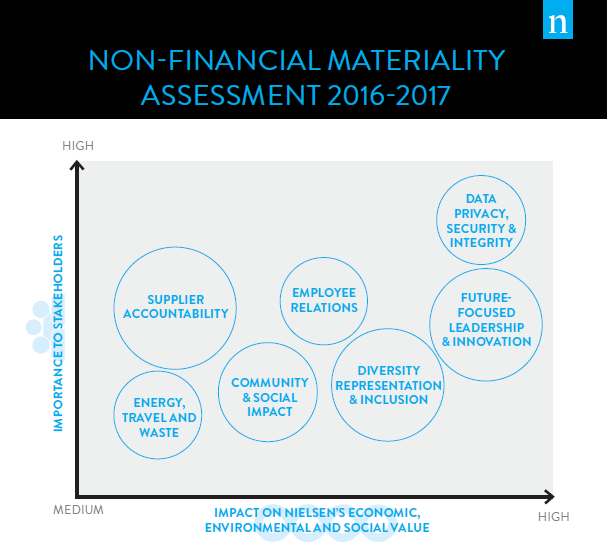
We compiled and reviewed stakeholder feedback to extract key issues and topics, ranking the importance to Nielsen and noting business and societal impacts as part of the process. We structured our analysis to align with GRI’s guidance to include societal and environmental impacts as a critical component in issue ranking. This approach is recognized through the dual axes included in the materiality matrix, noting Nielsen’s impact on society, the environment and stakeholders as well as each issue’s relative importance to stakeholders. Priority ranking was given to issues that Nielsen can take action to address based on our business’ core competencies and demonstrated strengths. More than 350 distinct topics were raised by stakeholders through this process; the top seven material issues in our matrix reflect a comprehensive compilation of these various areas.
We also reviewed the key issues that were raised in our 2014-2015 assessment to evaluate how progress has been made in the intervening years, and to identify where risks, challenges and opportunities still exist. Some of these issues remain on the 2016-2017 assessment but may have been redefined to reflect current circumstances and context; other issues may have dropped in position because their relative importance to stakeholders and society may have changed, or because of other developments (see “Update from 2014-2015 assessment” throughout for more information about our efforts to address these material issues from our 2014-2015 assessment).
Any issue on our matrix should be considered important to the company, regardless of its relative position on the matrix. In this updated assessment, we have transitioned from the twelve issues included in our 2014-2015 non-financial materiality assessment to the seven issues in our current non-financial materiality assessment. The issues that no longer appear exactly as they did in the 2014-2015 assessment are the following, in no particular order: Product and Service Responsibility, Business Ethics and Integrity, Transparency, Market Responsiveness and Proactivity, Company Integration, Public Policy, Data Use, and Responsible Growth & Supplier Accountability. All of these issues raised in our previous assessment have been integrated in some way into this updated 2016-2017 assessment in recognition of the natural connections across the new and updated areas included in this report.
Source: Feedback was solicited from source documentation and more than 200 internal and external stakeholders on a broad range of topics, including our company’s impact on the environment, society and the economy.
Top issues identified by the non-financial materiality assessment
Data privacy, security & integrity
Our approach: We reinforce our commitment to ensuring our data is protected, especially in light of the globally-recognized risks to data security overall. In speaking with our stakeholders, we recognize a particular interest in the processes used to conduct market research through mobile and digital sources. Other rising areas of stakeholder interest center around validation and ethics issues related to new, broadly-used research techniques.
We recognize our critical responsibility to scrupulously manage the data we collect. This includes, but is not limited to, the protection of privacy for our clients, employees and the consumers we measure; securing our data so that it is accessible only to authorized personnel for authorized purposes; and ensuring that our data is of the highest quality practicable. This is fundamentally linked to Nielsen’s role as a trusted provider for our clients and to our position as an independent measurement provider for the industries we serve. Beyond this 90-plus year commitment, we follow closely consumer attitudinal, legal and regulatory changes around the collection, use, and access of data.
Goal: Throughout 2017 we continue to adjust our policies, organizational responsibilities, and operating procedures as needed to respond to new laws and regulations including the European Union (EU)’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Update from 2014-2015 assessment: In 2016, we conducted and completed mandatory training for employees on “Global Information Security and Privacy Essentials.” We also harmonized Nielsen’s global internal privacy and data use policies, improved our data mapping process, enhanced our internal privacy resource website and online discussion forum, and designated additional internal privacy specialists in key countries around the world. To further our efforts in building an industry-leading Cyber Security program, we hired our first Global Chief Information Security Officer (CISO). More information about our overall approach to Data Privacy, Security & Integrity can be found in the “Our Clients” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report
We also updated Nielsen’s public-facing description of our privacy practices to reflect our new policy described in our updated privacy statement.
Learn more: More information about our approach to Data Privacy, Security & Integrity can be found in the “Our Clients” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report. Nielsen’s current privacy practices are described in our updated public-facing privacy statement.
Future-focused leadership & innovation
Our approach: We are committed to taking bold and swift new action in the face of change. Like our stakeholders, we recognize that innovation only counts as innovation if it’s delivered at the right time and in the right way; this is a critical component of what useful means to Nielsen within our overall values framework. Innovation is the foundation for our commitment to working with our clients to determine what’s next.
We continue to seek to introduce more innovative methodologies, products and solutions that help our clients have a complete understanding of the evolving consumer landscape, measuring what consumers are watching and what they are buying. We will continue to introduce solutions that not only measure our clients’ performance, but also help clients improve their business results. We do this through open dialogue with our clients and through strategic elements of our business like additive mergers and acquisitions, our Nielsen Innovate Fund, and our Nielsen Innovation Lab. We aim to be the best in the world at execution by remaining focused on our key strategic priorities, with innovation at the core of everything we do. This future-focused approach includes the adoption of new technologies, shifts in our internal company culture to encourage employees to be more innovative, and to more actively seek out business partnerships and acquisitions that provide value-added, innovative solutions.
Goal: In order to encourage our culture of innovation, by 2020 we plan to grow our commitment to regular training for all associates by at least 80% of associates taking at least one training program annually.
Update from 2014-2015 assessment: This area is connected to a number of issues that were raised in our previous assessment, particularly Market Responsiveness and Proactivity. We not only recognize the importance of proactively seeking out solutions to the changing needs of our clients, industries, and the broader marketplace, but we are also focused on acting as a pathbreaker into the future, helping Nielsen and our stakeholders to address the future more confidently and effectively. This focus on the future also includes our commitment to our associates; innovation for the future means developing our leaders today. One example is our nDigital training program through our internal myLearning platform; nDigital enables our associates to better understand the digital ecosystem our clients operate within and support the delivery of successful outcomes. Another example of how talent development contributes to our focus on innovation is our Innovate & Grow program open to all Operations associates; this program encourages associates to innovate no matter their role within the organization. Both this program and the Global Advance Development Program (GADP), focused on emerging leaders within Technology & Operations, help to retain talent, drive faster and more efficient client outcomes, reduce costs, and increase revenue.
Learn more: More information about our future-focused strategic direction can be found throughout our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Diversity representation & inclusion
Our approach: It is crucial that our organization is inclusive and reflects the diversity of the markets we measure. To accomplish this, we partner with a broad range of stakeholders, including our clients, suppliers, employees and senior leadership, as well as current and potential research sample panelists. We also ensure our methodology, data and insights are inclusive and representative of the diverse communities and demographics that we measure.
An example of this commitment can be found in our Diverse Intelligence Series reports, a collection of comprehensive insights regarding U.S. diverse consumers and their unique consumption and purchasing habits. Reports have been produced regarding African American, Hispanic/Latino, Asian, and LGBTQ consumers, and for the first time in 2016, consumers with disabilities.
Internally, we realize Diversity & Inclusion (D&I) is crucial to Nielsen’s growth, strength and ability to innovate. The mission of our D&I strategy, therefore, is to infuse D&I into the DNA of the company with a focus on accountability, career development, retention, supplier diversity and education/engagement. We also state very simply that we oppose discrimination on grounds including religion, race, ethnicity, gender, gender identity or expression, age, national origin, disability and sexual orientation. We define diversity as far more than what you see – it is the collection of different skills, experiences, talents and cultural backgrounds. And inclusion is defined as the ability to value and leverage these differences to achieve superior results.
Goal: At Nielsen, we have established a companywide minimum goal of 10% in annual spend with diverse suppliers globally. Each business unit has their own goals based on opportunities in their specific areas of spend. This goal is also shared with our suppliers through our supplier diversity Tier 2 program, where suppliers report their direct and indirect diversity spend to support our program. Supplier diversity performance against goals is shared in our Diversity & Inclusion annual report and presented to our External Advisory Council twice a year.
Learn more: More information about our approach to Diversity Representation & Inclusion can be found in our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report and our Nielsen Diversity & Inclusion Report.
Community & social impact
Our approach: Stakeholders expressed appreciation for Nielsen’s existing community efforts, alliances and partnerships through initiatives like Nielsen Cares, our global employee volunteer program, and Data for Good, through which we support initiatives such as Project 8, the data platform for forecasting developing human needs.
Nielsen’s community impact encompasses our role as a good corporate citizen and employer, our engagement in skills-based volunteerism, and our participation in in-kind giving with nonprofits. We also deploy our research expertise to provide insights to community leaders. We are aware that the data we collect from individuals in the community must be protected and used carefully no matter what the circumstances; we understand our responsibility relates to ensuring the representation of all communities.
Goals: Our goals in this area are focused on the long-term; from 2016 through 2020, our goal is to provide $50 million in value through pro bono projects and skills-based volunteering, including the donation of Nielsen data, and mobilizing our associates to volunteer a cumulative total of at least 300,000 hours in the communities where we live and work around the world. We have created a new Nielsen Foundation to support associate volunteering and giving, stakeholder support, and Data for Good and nonprofit grants.
Update from 2014-2015 assessment: Data is the foundation of our work and we believe it should be fundamental to advance social good. In our last non-financial materiality assessment, stakeholders mentioned an interest in learning more about how we are furthering our efforts to make a positive impact on the communities where we live and work, particularly through our global Nielsen Cares employee volunteer efforts and our pro bono data donations to nonprofits in key priority areas. In order to answer stakeholders’ questions about the impact of these efforts, we provided additional stories through a number of channels, including “Responsibility & Sustainability” features on Nielsen News Center, our 2016 Global Responsibility & Sustainability infographic, and the “Our Communities” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report. Our community impact efforts through Nielsen Cares reached record highs in 2016, engaging more than 23,000 employees through our annual Nielsen Global Impact Day (NGID) as well as through ongoing skills-based and hands-on volunteer opportunities. This is one part of our effort to enable our associates to personalize their Nielsen Employee Experience, providing unique ways to be themselves, make a difference, and grow with us.
We’ve committed to enhance the use of data to increase impact in reducing discrimination, easing global hunger, promoting STEM education and building stronger leadership in the social sector through our Data for Good initiatives such as Project 8, a global, digital information community where people come together to share, compare, analyze and discuss data and perspectives on sustainable development and evolving human needs. Nielsen is a significant contributor towards Project 8, based at The Demand Institute, providing leadership resources, data, and insights. We partnered with Accenture, Salesforce, and the UN Foundation to develop the Project 8 platform. Data for Good also includes our donation of data to the University of Chicago, in support of academic and social research. Through the University of Chicago, eligible academic researchers can apply to access a data warehouse of Consumer Panel Data and Retail Scanner Data to advance their research.
In 2015, we established the Nielsen Foundation to strengthen Nielsen communities by enhancing their ability to use data for social good, and to give back to our communities in ways that respond to social issues of concern to Nielsen associates and other stakeholders. The Foundation, funded by a one-time receipt of proceeds from a litigation settlement, has three main objectives: to encourage Nielsen associates to volunteer in their communities and engage in philanthropic activities, to enhance Nielsen’s relationships and its reputation as a good corporate citizen by enhancing the use of data and measurement to increase social impact, and to build knowledge through engaging in Foundation initiatives.
Learn more: More information about our approach to Community & Social Impact can be found in the “Our Communities” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Supplier accountability
Our approach: In line with our own expectations, our stakeholders expect Nielsen to manage and monitor the performance of our suppliers. We are committed to holding our suppliers to high standards in relevant environmental, social, and governance (ESG) areas, including human rights, integrity, diversity, ethics, and responsible business practices.
We have strengthened our overall approach to supply chain sustainability with a formal program, Nielsen Source Green, which was launched in 2016 to incorporate environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance in the management of our supply chain. The first year of the program completed in 2016 and focused on putting in place foundational elements aligned with best practices in sustainable sourcing including: establishing a system to measure and manage our suppliers’ ESG performance; embedding sustainability management in sourcing business processes; and connecting Nielsen’s program to leading industry-shaping collaborations. In 2017 and 2018, Nielsen plans to strengthen our ESG supply chain management even further at both the supplier level and product/service category level with specific, measurable key performance indicators and a track record of positive improvement over time. We recognize that sustainable supply chain management is one of the key ways that our company is delivering a societal impact that extends beyond a benefit to Nielsen. Nielsen’s purchasing power can be a powerful market force that contributes to addressing business challenges as well as social and environmental challenges.
Goals: Our current goals in this area are to include up to 100 of our top suppliers–or 50% of total sourceable spend with suppliers–in our supply chain sustainability program by 2018, up from more than a third of our spend in 2016. We have updated our Supplier Code of Conduct, and training will be provided to 100% of the Nielsen Strategic Partnerships and Sourcing Team as well as to 75% of our top strategic suppliers. We also plan to measurably raise awareness about our supply chain sustainability program internally through various communications channels throughout 2017 and beyond. Finally, we plan to establish an Environmentally Preferable Purchasing (EPP) policy and determine metrics to measurably increase our positive ESG impacts in each of the following areas of our spend: travel accommodations, air and ground transport, computers and office equipment, paper and printing, cleaning/janitorial services, event planning, and business process outsourcing (BPO) work.
Update from 2014-2015 assessment: In recognition of our goal to continue to improve the responsibility and representation of our suppliers, Nielsen’s diverse supplier spend in 2015 reached $75 million, representing a 24% year-over-year increase and 8% of Nielsen’s total sourceable spend. We also continued the work of our Nielsen Supplier Diversity Academy, started in 2014, which provides education and counsel to help diverse businesses prosper. These collaborations have resulted in over 200 jobs being created at minority-owned firms as a direct result of doing business with Nielsen. To give diverse businesses the tools they need to grow, the supplier diversity team has developed a slate of workshops that tap the expertise of Nielsen’s senior leaders across a variety of topics to share best practices and key strategies with the goal of helping diverse suppliers incorporate these lessons into their own businesses.
In 2016, Nielsen Source Green’s inaugural year, we asked 57 of our most strategic suppliers to complete an assessment to benchmark supplier ESG performance. Ninety-one percent of those suppliers participated, which exceeded the ambitious 70% target set for the first year of most programs. Among the suppliers who responded, 31% of them were evaluating their ESG performance for the first time. Additionally, ESG criteria were updated or added in the following sourcing processes: RFPs, contract language, and periodic business reviews and compliance disclosure. We updated our Supplier Code of Conduct to reflect our current expectations for supplier accountability. We have also developed a complementary toolkit of capacity-building resources and training to assist suppliers in meeting these requirements on an ongoing basis.
To demonstrate our commitment to leadership in supply chain sustainability, Nielsen joined the Sustainable Purchasing Leadership Council (SPLC) and the Electronic Industry Citizenship Coalition (EICC), as well as adapting the EICC Code of Conduct as the basis for Nielsen’s Supplier Code of Conduct. We are also a founding member of the Global Impact Sourcing Coalition, which focuses on innovative sourcing efforts to build a more inclusive global supply chain and meet our business needs while providing a pathway for workers out of extreme poverty. Finally, Nielsen was represented on the technical advisory group for ISO 20400, the new ISO Sustainable Procurement Standard. More information about our overall approach to supply chain sustainability is included in the “Supply Chain” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Learn more: More information about our approach to Supplier Accountability can be found in the “Supply Chain” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Energy, travel & waste
Our approach: In speaking with our stakeholders, we have identified energy, business travel and waste (particularly electronic waste, or e-waste, and paper waste) as the three largest environmental issues for Nielsen. These three distinct issues generally reflect the material environmental issues of other Professional Services firms. We recognize that Nielsen has an opportunity to expand on our commitment to reduce and maximize these and other aspects of our overall environmental footprint. Analysis continues to fully quantify and report the significance of each of these issues for Nielsen.
Nielsen’s energy use is both direct (consumed at our company-owned or rented offices and data centers) and indirect (shared and/or contracted data center use). Water use is not significant at this point in terms of Nielsen’s direct operations; however, it is recognized as an important societal issue. External stakeholders asked for more information about our greenhouse gas emissions (especially Scope 3), as well as energy use and reduction efforts related to our data centers. They have also requested that we set environmental goals and targets with an expanded data set to reflect our complete global footprint. By broadening our data collection efforts and working to improve our own environmental performance, we hope to deliver broader benefits to the planet and society as a whole, doing Nielsen’s part to address issues related to climate change. In terms of our Scope 3 emissions reduction efforts specifically, all Nielsen associates are encouraged to exhaust all travel alternatives such as video conferencing, virtual meetings, and conference calls before requesting permission to travel. Travel alternatives are systematically highlighted in our online booking tool with automated pop-up messaging and links to video conferencing details. Nielsen also prioritizes conducting business with socially responsible travel suppliers; we do this by tracking, monitoring and engaging our travel suppliers on their environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance through a third-party online platform.
Goals: By 2020, our goal is to reduce our global energy use per square foot of facility space by 5%. We are using 2015 North American data as a baseline for this as we expand our data collection efforts globally. Additionally, in 2018, Nielsen plans to join the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) Supply Chain Program to manage the risks and opportunities associated with climate change in a standardized way across our supply chain. This participation will help Nielsen improve its supply chain transparency and environmental performance and facilitate our suppliers gaining opportunities from increased energy efficiency, leading to decreased costs and better preparedness for climate-related risks.
Update from 2014-2015 assessment: In our 2014-2015 non-financial materiality assessment, our stakeholders challenged us to do more in the areas of environmental management and reporting. To address this opportunity, we took a number of actions that are highlighted throughout the “Our Environment” section of the Nielsen Global Responsibility Report. In 2015, we began a multi-year plan to upgrade data storage technology and consolidate operations—all with an eye on long-term performance improvements, emissions reductions and cost savings. In 2016, projects to upgrade to all-flash storage, virtualize our systems, consolidate our data centers and further simplify our processes led to 7.7 million kilowatt hours (kwh) in power savings and 7.2 million kg in carbon dioxide emissions avoided. In 2016, we expanded our data collection efforts to include our Latin American presence in addition to North America; we plan to continue the global expansion of our environmental sustainability data in the years to come. In order to ensure more location-specific attention is paid to this area, we also added Climate Change as a risk in our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework. For the first time, we responded to the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), joining close to 6,000 companies in over 90 countries, to disclose our enterprise-wide greenhouse gas emissions and related mitigation actions; we have also joined CDP as a corporate member.
Learn more: More information about our approach to Environmental Sustainability efforts, including as it relates to Energy, Travel & Waste, can be found in the “Our Environment” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Employee relations
Our approach: Through interviews and focus groups, we have identified opportunities for greater strategic engagement with employees regarding decisions that affect them, including but not limited to: maintaining a flexible work environment, performance rewards and compensation, workspace and equipment enhancements, integrating new employees into Nielsen through acquisitions, and further growing our broad range of career advancement opportunities. A rising issue for employees in the Professional Services industry in general is a need for more training to upgrade skills in the areas of digital and mobile measurement and innovation. External stakeholders expressed a desire for more information about our ongoing employee retention and turnover mitigation efforts as well as greater transparency around more specific human capital goals.
We have an inherent responsibility to provide a safe, healthy and fair work environment for all of our employees. Beyond this, we also endeavour to provide unique career and education opportunities, compensate fairly based on a culture of meritocracy, demonstrate support for diversity and inclusion, and encourage employee satisfaction. We recognize that in order to continue to grow our business around the world, we need to continue to find innovative ways to hire and train employees with the right skills and expertise.
Goal: Recognizing the importance of diversity and inclusion for our global workforce, we offer specific training on diversity and inclusion for managers and associates. Partnering with a diverse supplier, we’ve had 93% of our global managers complete the core program since 2014, focused on expanding the conversation around diversity and inclusion. The program is designed to help managers better understand the importance of diversity and inclusion as a business imperative and learn key messaging and skills for fostering an inclusive work environment. Phase two of this series focuses on Unconscious Bias training. Our aim is to have at least 80% of all global associates complete at least one of the diversity and inclusion trainings by 2019, while continuing to offer additional resources that support the learning after the formal training is completed.
Update from 2014-2015 assessment: In 2016, we shared more information about our overall approach to employee relations through the “Our People” section of the Nielsen Global Responsibility Report, including programs, policies and efforts across areas like health and wellness, training and education, talent acquisition, diversity and equal opportunity, and People Analytics. We have also updated our Nielsen Careers website to include more comprehensive information about company culture and employee stories, particularly as it relates to the three tenets of our Nielsen Employee Experience: you can be yourself, you can make a difference, and you can grow with us. In 2016 we also launched the Nielsen Global Support Fund to help associates facing financial hardship immediately after a qualified disaster or an unforeseen personal hardship. The Nielsen Global Support Fund is administered by an external charitable organization with full oversight for all grant-based activities, including application review and grant approval.
Performance reviews and job opportunities in particular were shared as top areas of interest for our employees in our last non-financial materiality assessment. To address this, Nielsen introduced “Check-Ins” in 2015 to encourage more real-time, ongoing conversations between associates and their managers about performance, their Nielsen employee experience overall, and future career opportunities. In 2016, we updated our performance evaluation criteria from a 4-point rating scale to 5 performance narratives in conjunction with Growth Potential, that provides a more holistic approach to exploring opportunities with an employee’s current role or moving into a new one.
Diversity and Inclusion was one of the strongest themes from our first non-financial materiality assessment, cutting across all of our top material areas. In response, Nielsen took action in a number of different ways, including the release of our first Diversity and Inclusion Report which catalogues our programs and achievements in the ways that diversity and inclusion is a fundamental pillar across employee and supplier relations and community outreach. In terms of organizational risk management, Diversity & Inclusion and Health, Safety and Human Rights were added as risks in our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) framework, which inherently increases attention and cross-functional collaboration. Key highlights since our last assessment in this area include the launch of our Global Diversity Council in 2017 to highlight and share best practices in the area of Diversity and Inclusion globally. We also continued to expand the global reach of our Employee Resource Groups (ERGs); ERG membership now includes more than 6,700 employees globally. The launch of our first Nielsen Black Employee Forum also marked a new step forward, particularly in our continued efforts to develop and retain diverse talent. By providing visibility, access and opportunity to our associates, this professional development opportunity sought to increase engagement and retention and empower associates to strengthen networks through access to senior leaders, cultural events and business strategy workshops.
In 2015, we introduced an educational initiative to provide unconscious-bias training to leaders to help recognize and mitigate our impact on daily leadership decisions and workplace environments. As a result, we had a record number of employees (93% across 66 countries) complete Diversity and Inclusion training. Additionally, the company launched a new tool to give Human Resources and senior leaders a closer look at key employee metrics such as associate demographics, diversity hiring rates, role changes and job openings. This information further facilitates training offerings that better help employees upgrade their skills and readiness for promotion.
Learn more: More information about our approach to Employee Relations can be found in the “Our People” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report.
Response to key stakeholder issues identified in the 2014-2015 non-financial materiality assessment
After completing our 2014-2015 non-financial materiality assessment, we initiated actions to respond to stakeholder feedback. These areas also provided the foundation for our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report, published in 2016. Information about these relevant actions is included above for issues that were raised again in our 2016-2017 non-financial materiality assessment; information about relevant actions taken to address issues that were not raised again in this more recent assessment is included below.
Business ethics and integrity
We plan to release an updated Nielsen Code of Conduct during 2017. The updated Code of Conduct will provide employees with specific examples and guidance related to our overarching commitment to “Integrity in Action.” Also in 2017, we plan to update our global human rights guidelines to include more specific information about our approach to monitoring, managing and tracking potential human rights impacts and risks across our business and supply chain.
Early in 2017, we launched an internal “Integrity Ambassador” program to provide additional support for our overall Compliance & Integrity program. Integrity Ambassadors will serve as local-country resources to raise awareness about compliance and integrity resources and initiatives. We are currently piloting the program in approximately 20 countries and plan to expand this program to all of our markets in the coming years.
Market responsiveness and proactivity, and company integration
When the areas of Company Integration and Market Responsiveness & Proactivity were raised in our first non-financial materiality assessment in 2014-2015, the core issue was a need for further integration across our full portfolio of products, services, and teams to ensure we are addressing client and industry needs proactively and effectively.
From 2014-2016, Nielsen acquired 18 companies to add to our growing expertise in digital and mobile measurement. Through our newly consolidated Corporate Development and Strategy team, we plan to continue to align our strategic approach as it relates to mergers and acquisitions, Nielsen Ventures, strategic initiatives and overall corporate strategy. In 2016, we also launched our Nielsen Connected Partner Program to open up access for the first time to our global Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) data for a select group of partners that provide added value for our clients. These Connected Partners make it easier for our clients to leverage our wealth of data without needing to source new partners separately. Another important factor is our ability to remain proactive in responding to the current and future needs of our clients through Nielsen’s foundational investments in development and innovation protection demonstrated by building out the breadth and depth of our intellectual property. Our active granted U.S. intellectual property portfolio has grown elevenfold (1013%) over the past eight years; Nielsen now holds more than 2,950 worldwide patents and patent applications, with over 913 granted in the U.S.
We have also done more to share how various teams and aspects of our business connect in integrated ways. Our ongoing Nielsen Around the World video series highlights the employees who help make our data and insights possible from around the world, and it gives clients and others an inside look into how we work on the ground. Our newly-launched Nielsen Next video series also provides clients and other stakeholders with a better understanding of how Nielsen’s data provides the science behind what’s next.
Product and service responsibility
When this topic was raised by stakeholders in our 2014-2015 non-financial materiality assessment, it encompassed Nielsen’s responsibility to deliver timely and insightful research that fully reflects demographic diversity. We highlighted our efforts in this regard in our first Nielsen Diversity & Inclusion Report, published in 2016. Within that report, we shared our collaborative efforts with more than 200 different community organizations as a way to support recruitment of diverse panel and survey participants; this contributes to the effectiveness of our full product portfolio. In terms of other efforts to strengthen our overall product offerings, in 2016 we also expanded e-commerce measurement to the U.S., announced plans to enhance our local television measurement and Scarborough qualitative consumer insights in the U.S. across all 210 markets by enabling true electronic measurement, and added out-of-home measurement.
Public policy
Nielsen’s strategic engagement with governments, regulators, and other external stakeholders advances our business and community interests. We continued to build relationships to position Nielsen as a trusted advisor in policy discussions and to advocate for Nielsen’s interests and discussed our policy efforts in the “Public and Policymakers” section of our Nielsen Global Responsibility Report. We are focused on creating the best environment possible for Nielsen’s business to thrive.
Transparency
Transparency is essential to assure our clients and other stakeholders that our research methodologies, data and insights are trustworthy. To address this, Nielsen has increased communications about the methodology and processes we use to collect and analyze consumer data. Some examples of these communications efforts range from “How We Measure”, Perspectives on Retail Technology, our recently-launched Journal of Measurement, regular features on Nielsen News Center, our revised public-facing Digital Measurement Privacy Statement, and our ongoing Nielsen Around the World series. Our aim is to more comprehensively illustrate what it takes to capture and analyze the data that underpins our best-in-class global measurement.
Data use
In our first non-financial materiality assessment, stakeholders expressed their expectation that Nielsen both remain fully aware of how the data we collect is used across various contexts, and to seek projects that create positive social, environmental and business value. In terms of leveraging our data assets to further thought leadership efforts in key areas of value to society, some relevant reports from 2016 covered topics like the economic power and preferences of a diverse range of consumer groups through our Diverse Intelligence Reports; the growing influence of Hispanic consumers; health, wellness and obesity trends in Asia; trends in organic food consumption; the growing consumer demand for ingredients transparency; and the demand for greener cleaning products, among others.
